In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, businesses face an ever-increasing array of threats that can compromise sensitive data and disrupt operations. Cyber insurance has become a critical component of risk management strategies, offering a financial safety net in the event of a cyber incident. However, the role of cyber insurance companies extends far beyond providing monetary compensation. These insurers are uniquely positioned to promote advanced cybersecurity frameworks, such as Zero Trust and Unified Zero Trust platforms, to enhance overall security postures and reduce the likelihood of breaches.
Understanding Zero Trust
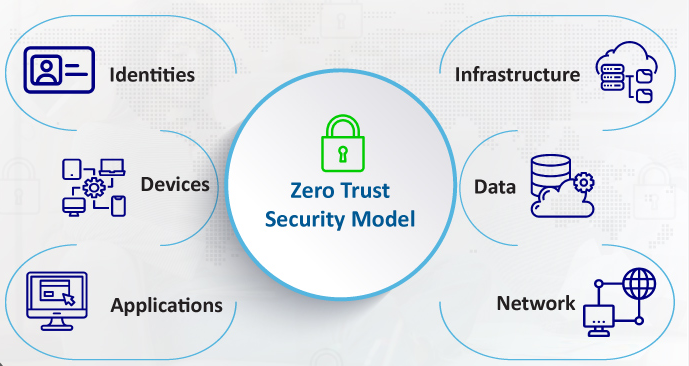
The Zero Trust security model operates on the principle that no entity, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. Every access request must be verified, authenticated, and authorized before granting access to resources. This approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within a network, even if an attacker manages to breach the perimeter defenses.
The Shift to Unified Zero Trust Platforms
A Unified Zero Trust platform integrates various security components into a cohesive system that enforces Zero Trust principles across the entire IT environment. Platforms like Unified Zero Trust Platforms offer comprehensive solutions that encompass Zero Trust principles, ranging from endpoint security and network security to cloud workloads and continuous monitoring. This unified approach ensures that all aspects of the IT infrastructure are protected under the same rigorous security standards, providing a holistic defense against cyber threats.
Dangers of Promoting Non Zero Trust Cybersecurity Solutions
Despite the clear benefits of Zero Trust, some cyber insurance companies may continue to promote traditional, non-Zero Trust cybersecurity solutions, such as default allow models. This approach can pose significant risks:
1. Increased Vulnerability to Attacks
Traditional security models often rely on perimeter defenses and assume that entities within the network can be trusted. This assumption can lead to increased vulnerability to attacks, as once an attacker breaches the perimeter, they may move laterally within the network with relative ease.
2. Higher Likelihood of Breaches
Non-Zero Trust solutions can create blind spots and gaps in security coverage. Without continuous verification and strict access controls, unauthorized access can go undetected, leading to a higher likelihood of data breaches and other cyber incidents.
3. Inconsistent Security Posture
Default allow solutions may lead to inconsistent security postures across different parts of an organization. Some areas may have stronger protections than others, creating weak points that attackers can exploit.
4. Reactive Rather Than Proactive Security
Non-Zero Trust models tend to be reactive, responding to threats after they have already infiltrated the network. In contrast, Zero Trust models are proactive, constantly verifying and monitoring all access requests to prevent unauthorized access before it occurs.
5. Increased Financial and Reputational Risk
By promoting non-Zero Trust solutions, cyber insurance companies may inadvertently increase the financial and reputational risks for their clients. Breaches can lead to significant financial losses, regulatory fines, and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Proof That Legacy Products Are Not Working
The following data table illustrates the rising costs and number of data breaches despite significant increases in cybersecurity spending over the past decade. This evidence underscores the ineffectiveness of traditional, non-Zero Trust solutions:
| Year | Cybersecurity Spending (USD Billions) | Number of Data Breaches | Cost of Breaches (USD Billions) |
| 2014 | 71.1 | 1579 | 3.5 |
| 2015 | 81.6 | 1632 | 3.8 |
| 2016 | 90.0 | 1693 | 4.0 |
| 2017 | 101.5 | 1780 | 4.3 |
| 2018 | 115.2 | 1997 | 4.8 |
| 2019 | 130.1 | 2107 | 5.1 |
| 2020 | 145.7 | 2305 | 5.6 |
| 2021 | 170.4 | 2220 | 6.1 |
| 2022 | 186.4 | 2400 | 6.5 |
| 2023 | 198.0 (partial year estimate) | 1802 (partial data) | 7.0 (estimate) |
As seen in the table, cybersecurity spending has nearly tripled from 2014 to 2023, yet the cost of data breaches has also almost doubled. This trend highlights the inadequacies of legacy cybersecurity products and the urgent need for a paradigm shift towards more effective, comprehensive solutions like Zero Trust.
Conclusion
In the battle against cyber threats, the collaboration between cyber insurance companies and businesses is paramount. By promoting the adoption of Zero Trust and Unified Zero Trust platforms, insurers can play a pivotal role in enhancing cybersecurity defenses and reducing the overall risk of cyber incidents. This proactive approach not only benefits the insured companies by providing better protection but also helps insurance companies by lowering the likelihood of costly claims. As the cyber threat landscape continues to evolve, the integration of advanced security frameworks and robust insurance coverage will be essential in safeguarding the digital assets of organizations worldwide. Conversely, continuing to promote non-Zero Trust solutions can leave organizations vulnerable and expose them to greater risks, underscoring the need for a paradigm shift towards more resilient and comprehensive cybersecurity strategies.